6. Building a Database Test Plan¶
In this section, you will learn how to create a basic Test Plan to test a database server. You will create fifty users that send 2 SQL requests to the database server. Also, you will tell the users to run their tests 100 times. So, the total number of requests is (50 users) x (2 requests) x (repeat 100 times) = 10'000 JDBC requests. To construct the Test Plan, you will use the following elements: Thread Group, JDBC Request, Summary Report.
6.1 Adding Users¶
The first step you want to do with every JMeter Test Plan is to add a Thread Group element. The Thread Group tells JMeter the number of users you want to simulate, how often the users should send requests, and how many requests they should send.
Go ahead and add the ThreadGroup element by first selecting the Test Plan, clicking your right mouse button to get the Add menu, and then select .
You should now see the Thread Group element under Test Plan. If you do not see the element, then expand the Test Plan tree by clicking on the Test Plan element.
Next, you need to modify the default properties. Select the Thread Group element in the tree, if you have not already selected it. You should now see the Thread Group Control Panel in the right section of the JMeter window (see Figure 6.1 below)
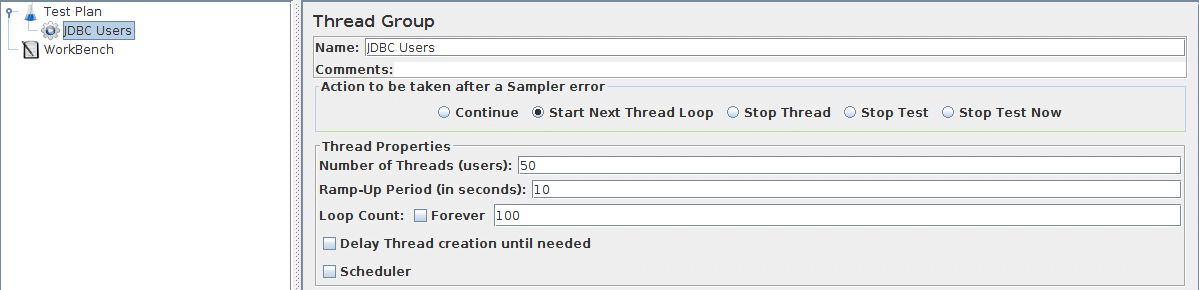
Start by providing a more descriptive name for our Thread Group. In the name field, enter JDBC Users.
Next, increase the number of users to 50.
In the next field, the Ramp-Up Period, leave the value of 10 seconds. This property tells JMeter how long to delay between starting each user. For example, if you enter a Ramp-Up Period of 10 seconds, JMeter will finish starting all of your users by the end of the 10 seconds. So, if we have 50 users and a 10 second Ramp-Up Period, then the delay between starting users would be 200 milliseconds (10 seconds / 50 users = 0.2 second per user). If you set the value to 0, then JMeter will immediately start all of your users.
Finally, enter a value of 100 in the Loop Count field. This property tells JMeter how many times to repeat your test. To have JMeter repeatedly run your Test Plan, select the Forever checkbox.
See Figure 6.2 for the completed JDBC Users Thread Group.
6.2 Adding JDBC Requests¶
Now that we have defined our users, it is time to define the tasks that they will be performing. In this section, you will specify the JDBC requests to perform.
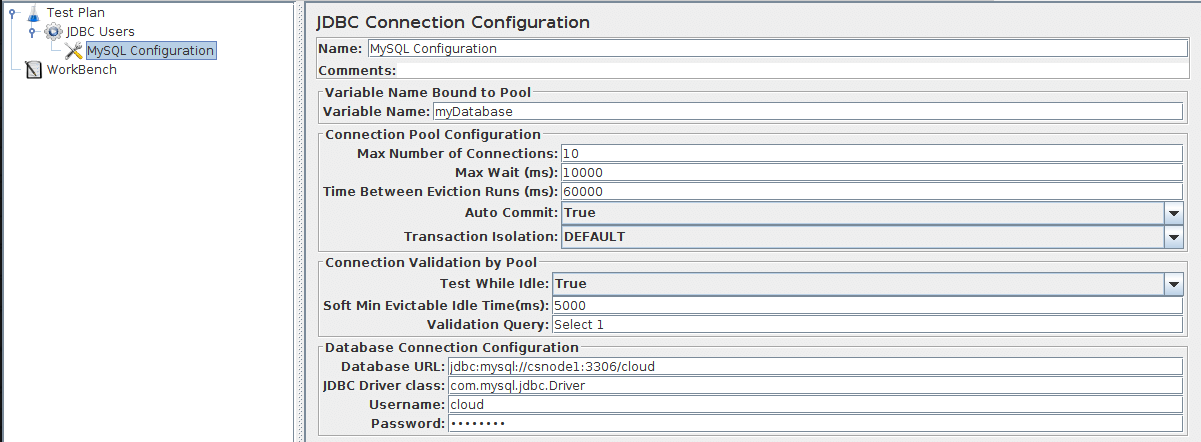
Begin by selecting the JDBC Users element. Click your right mouse button to get the Add menu, and then select . Then, select this new element to view its Control Panel (see Figure 6.3).
Set up the following fields (these assume we will be using a MySQL database called 'cloud'):
- Variable name (here: myDatabase) bound to pool. This needs to uniquely identify the configuration. It is used by the JDBC Sampler to identify the configuration to be used.
- Database URL: jdbc:mysql://ipOfTheServer:3306/cloud
- JDBC Driver class: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- Username: the username of database
- Password: password for the username
The other fields on the screen can be left as the defaults.
JMeter creates a database connection pool with the configuration settings as specified in the Control Panel. The pool is referred to in JDBC Requests in the 'Variable Name' field. Several different JDBC Configuration elements can be used, but they must have unique names. Every JDBC Request must refer to a JDBC Configuration pool. More than one JDBC Request can refer to the same pool.
Selecting the JDBC Users element again. Click your right mouse button to get the Add menu, and then select . Then, select this new element to view its Control Panel (see Figure 6.4).
In our Test Plan, we will make two JDBC requests. The first one is for select all 'Running' VM instances, and the second is to select 'Expunging' VM instance (obviously you should change these to examples appropriate for your particular database). These are illustrated below.
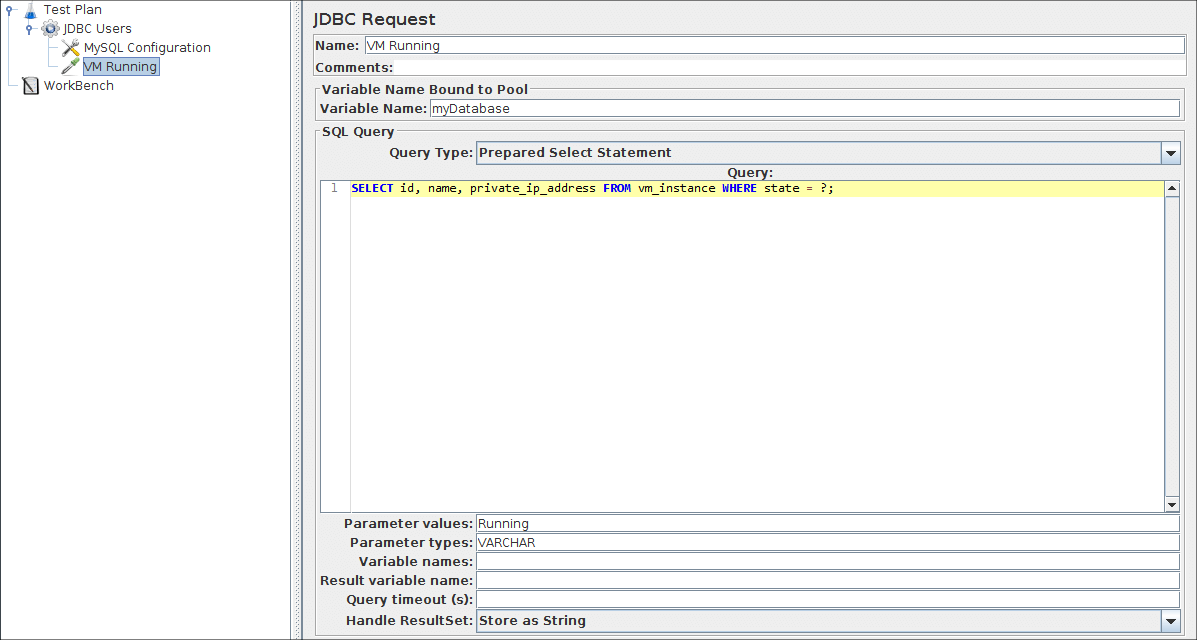
Start by editing the following properties (see Figure 6.5):
- Change the Name to 'VM Running'.
- Enter the Pool Name: 'myDatabase' (same as in the configuration element)
- Enter the SQL Query String field.
- Enter the Parameter values field with 'Running' value.
- Enter the Parameter types with 'VARCHAR'.
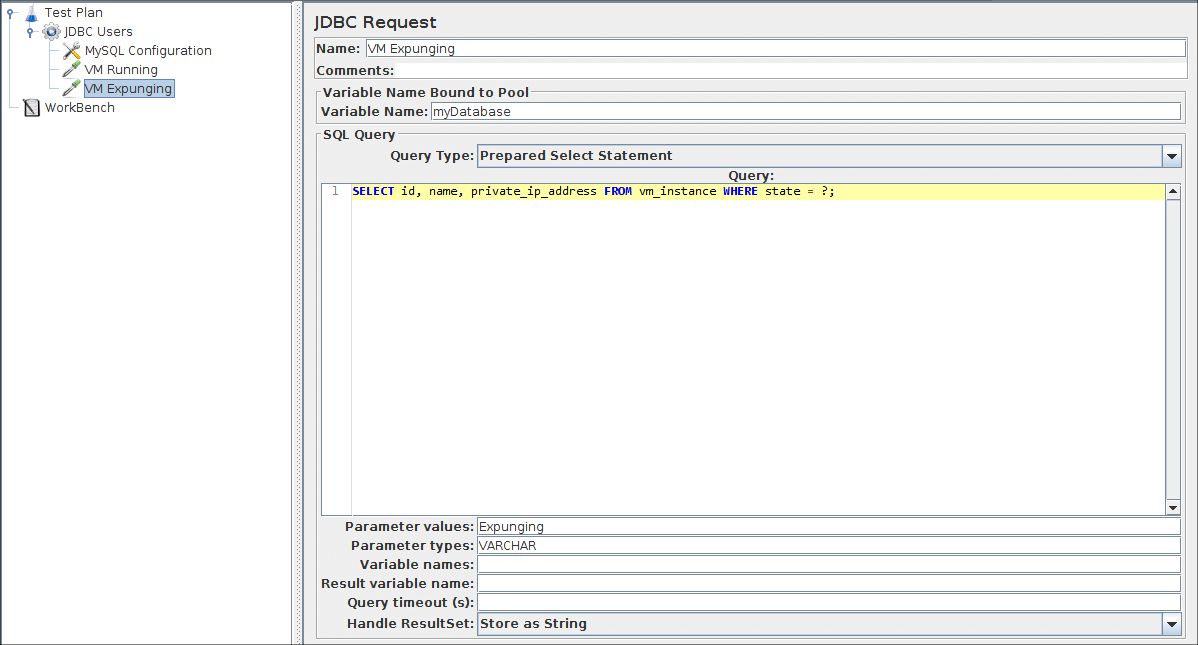
Next, add the second JDBC Request and edit the following properties (see Figure 6.6):
- Change the Name to 'VM Expunging'.
- Change the value of Parameter values to 'Expunging'.
6.3 Adding a Listener to View/Store the Test Results¶
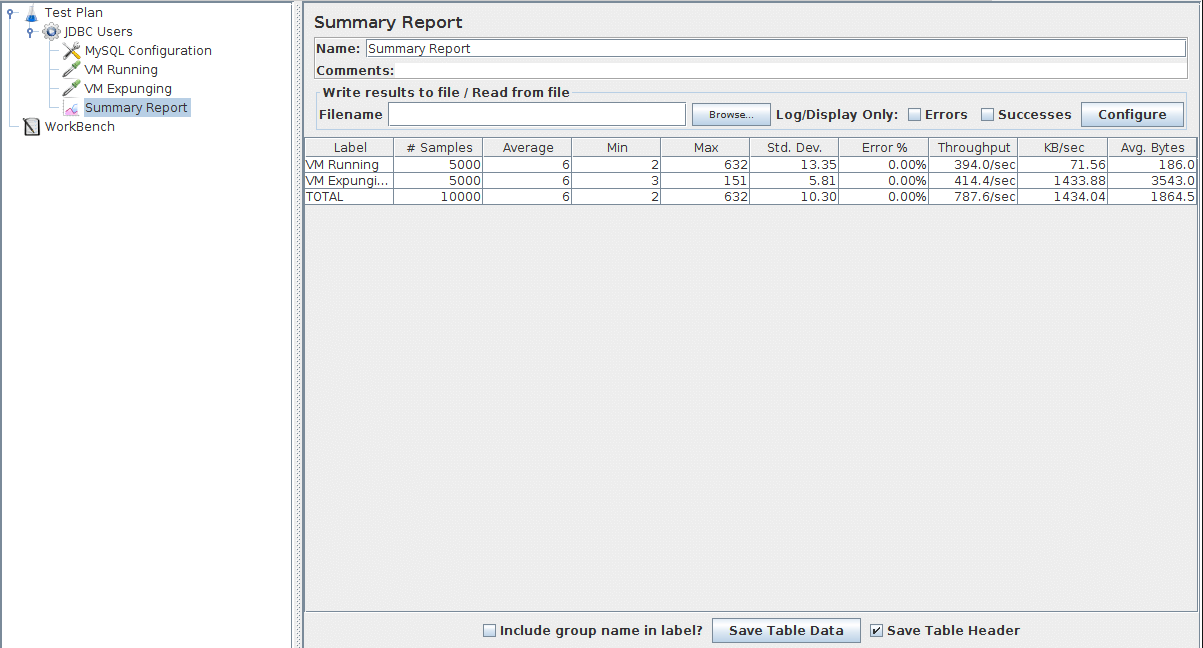
The final element you need to add to your Test Plan is a Listener. This element is responsible for storing all of the results of your JDBC requests in a file and presenting the results.
Select the JDBC Users element and add a Summary Report listener ().
Save the test plan, and run the test with the menu or Ctrl + R
The listener shows the results.